The Participation of the Population of Huai Phuang District, Kalasin Province in the Prevention and Control of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever
Main Article Content
Abstract
การวิจัยครั้งนี้มีวัตถุประสงค์เพื่อ 1) ศึกษาระดับการมีส่วนร่วมในการป้องกันและควบคุมโรคไข้เลือดออกของประชาชน 2) ศึกษาความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างลักษณะทางประชากร ความรู้เรื่องโรคไข้เลือดออก การสนับสนุนทางสังคม และอิทธิพลทางสังคมกับการมีส่วนร่วมในการป้องกันและควบคุมโรคไข้เลือดออกของประชาชน ประชากรและกลุ่มตัวอย่างคือตัวแทนครัวเรือนในอำเภอห้วยผึ้ง จำนวน 7,027 คนและ 240 คน ตามลำดับ โดยการสุ่มอย่างเป็นระบบเครื่องมือที่ใช้เป็นแบบสอบถามวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลโดยใช้สถิติ ร้อยละ ค่าเฉลี่ย ส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐาน ทดสอบสมมติฐานโดยใช้ไคส-แควร์และค่าสัมประสิทธิ์สหสัมพันธ์ของเพียร์สันผลการศึกษาพบว่าประชาชนมีระดับการมีส่วนร่วมในการป้องกันและควบคุมโรคไข้เลือดออกอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง (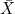 = 2.94, S.D = 0.30) แยกเป็นมีส่วนร่วมในขั้นตอนการค้นหาปัญหา สาเหตุของปัญหาอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง มีส่วนร่วมในขั้นตอนการตัดสินใจและวางแผนดำเนินการอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง (
= 2.94, S.D = 0.30) แยกเป็นมีส่วนร่วมในขั้นตอนการค้นหาปัญหา สาเหตุของปัญหาอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง มีส่วนร่วมในขั้นตอนการตัดสินใจและวางแผนดำเนินการอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง ( = 2.66, S.D = 0.19) มีส่วนร่วมในขั้นตอนการดำเนินงานอยู่ในระดับสูง และมีส่วนร่วมในขั้นตอนติดตามและประเมินผลอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง ปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับการมีส่วนร่วมในการป้องกันและควบคุมโรคไข้เลือดออกของประชาชน อำเภอห้วยผึ้งจังหวัดกาฬสินธุ์ ได้แก่ รายได้ต่อเดือน ระยะเวลาที่อาศัยในชุมชน ตำแหน่งทางสังคมการสนับสนุนทางสังคม และอิทธิพลทางสังคม อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ 0.05
= 2.66, S.D = 0.19) มีส่วนร่วมในขั้นตอนการดำเนินงานอยู่ในระดับสูง และมีส่วนร่วมในขั้นตอนติดตามและประเมินผลอยู่ในระดับปานกลาง ปัจจัยที่มีความสัมพันธ์กับการมีส่วนร่วมในการป้องกันและควบคุมโรคไข้เลือดออกของประชาชน อำเภอห้วยผึ้งจังหวัดกาฬสินธุ์ ได้แก่ รายได้ต่อเดือน ระยะเวลาที่อาศัยในชุมชน ตำแหน่งทางสังคมการสนับสนุนทางสังคม และอิทธิพลทางสังคม อย่างมีนัยสำคัญทางสถิติที่ระดับ 0.05
The study has two main objectives 1) to investigate the level of participation by members of a community in the prevention and control of dengue hemorrhagic fever. 2) to investigate the community’s understanding of the relationships between knowledge of dengue hemorrhagic fever, social support, social facilitation with prevention, and control of dengue hemorrhagic fever. Data were collected from 240 households in Huai Phung District Kalasin Province, by questionnaire. The data consisted of percentage, mean, standard deviation, maximum, minimum. Chi-square test and Pearson’s product moment correlation coefficient were the statistical methods used to hypothesize testing. The results of the study showed that the sample group had a mid-level understanding of the prevention and control of dengue hemorrhagic fever. Mid-level consisted of participation in decision and planning and the participation of performance appraisals. The relationships and people’s participation in the prevention and control of dengue hemorrhagic fever revealed that income per month, length of time in the community, social position, social support and social facilitation were determining factors.
Article Details
Section
Articles (บทความ)

