Developing a Model to Enhance Customer Loyalty in the Restaurant Business through Digital Transformation, Focusing on Risk and Image
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.57260/csdj.2025.278778Keywords:
Digital transformation, Customer loyalty, Restaurant industry, Perceived risk, Restaurant imageAbstract
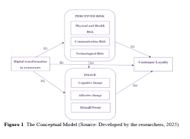
engagement and operational practices. This study critically examines how digital innovations—such as online ordering systems, mobile applications, and automated services—affect customer loyalty, focusing on the mediating roles of perceived risks and restaurant image. Targeting Thai consumers in Bangkok, this study adopts a mixed-methods approach to gain both breadth and depth of understanding. A structured survey (405 valid responses) was analyzed using Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) to test hypothesized relationships. To complement the quantitative findings, 12 semi‐structured interviews with restaurant owners, managers, and digital experts provided contextual insights and practical perspectives, enhancing the study’s validity through methodological triangulation. Findings reveal that digital transformation enhances customer loyalty by strengthening the restaurant’s image and mitigating perceived risks. However, challenges such as technological failures, data security concerns, and diminished personal interaction continue to pose significant barriers. The study reveals that effective digital strategies enhance customer satisfaction, but managing technological risks is crucial for maintaining trust and loyalty in the digital dining environment.
Downloads
References
Allen, I. E., & Seaman, C. A. (2007). Likert scales and data analyses. Quality Progress, 40(7), 64–65. Retrieved from https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=2559587
Bentler, P. M., & Chou, C. P. (1987). Practical issues in structural equation modeling. Sociological Methods & Research, 16(1), 78–117. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1177/0049124187016001004
Bitner, M. J., Brown, S. W., & Meuter, M. L. (2000). Technology infusion in service encounters. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 28(1), 138–149. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1177/0092070300281013
Breugelmans, E., & Liu Thompkins, Y. (2017). The effect of loyalty program expiration policy on consumer behavior. Marketing Letters, 28(4), 537–550. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1007/s11002-017-9438-1
Byrne, B. M. (2016). Structural equation modeling with Amos: Basic concepts, applications, and programming. (3rd ed.). Routledge. Retrieved from https://www.routledge.com/Structural-Equation-Modeling-With-AMOS-Basic-Concepts-Applications-and/Byrne/p/book/9781138797031?utm_source=chatgpt.com
Chen, P. J., & Kerstetter, D. L. (1999). International students’ image of rural Pennsylvania as a travel destination. Journal of Travel Research, 37(3), 256–266. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1177/004728759903700307
Chen, L., & Wang, R. (2016). Trust development and transfer from electronic commerce to social commerce: An empirical investigation. American Journal of Industrial and Business Management, 6(5), 568–576. Retrieved from https://www.scirp.org/journal/paperinformation?paperid=66436
Chew, E. Y . T., & Jahari, S. A. (2014). Destination image as a mediator between perceived risks and revisit intention: A case of post-disaster Japan. Tourism Management, 40, 382–393. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2013.07.008
Choi, T. M., He, Y., & Cheng, S. W. (2020). Managing digital risks in the hospitality industry: The impact of security and reliability on customer trust and repeat business. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 88, 102502. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102502
Cochran, W. G. (1977). Sampling techniques. (3rd ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
Creswell, J. W., & Plano Clark, V. L. (2018). Designing and conducting mixed methods research . (3rd ed.). SAGE Publications. Retrieved from https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=2697821
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319–340. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.2307/249008
DeLone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (2003). The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: A ten-year update. Journal of Management Information Systems, 19(4), 9–30. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1080/07421222.2003.11045748
DeVellis, R. F. (2017). Scale development: Theory and applications. (4th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Dinev, T., Hart, P., & Mullen, M. R. (2015). Internet privacy concerns and beliefs about information sharing: A review of the literature. In T. Dinev & P. Hart (Eds.), Proceedings of the 48th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (pp. 2728–2736).
Discover Global Network. (2023). Digital transformation in restaurants: Embracing contactless payments. Discover Global Network Insights. Retrieved from https://insights.discoverglobalnetwork.com/insights/digital-transformation-in-restaurants
Esposito, B., Sessa, M. R., Sica, D., & Malandrino, O. (2022). Service innovation in the restaurant sector during COVID 19: Digital technologies to reduce customers’ risk perception. The TQM Journal, 34(7), 134–164. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1108/TQM-01-2022-0016
Etikan, I., Musa, S. A., & Alkassim, R. S. (2016). Comparison of convenience sampling and purposive sampling. American Journal of Theoretical and Applied Statistics, 5(1), 1–4. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajtas.20160501.11
Fetters, M. D. (2019). The mixed methods research workbook: Activities for designing, implementing, and publishing projects. SAGE Publications.
Frontiers in Psychology. (2022). Digital transformation knowledge and resources increase perceived risk and benefits: implications for brand trust and image. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, 1017750. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1017750
Gursoy, D., & Chi, C. G. (2020). Effects of COVID 19 pandemic on the hospitality industry: Review of the current situations and a research agenda. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 29(5), 527–529. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1080/19368623.2020.1788231
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2006). Multivariate data analysis. (6th ed.). Pearson Prentice Hall. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1057/9781137484956_11
Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2011). Multivariate data analysis. (7th ed.). Pearson Prentice Hall.
Helal, M. Y. I. (2023). The impact of digital transformation on perceived hedonic/utilitarian value and brand loyalty in fast-food contexts. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology, 14(5), 893–907. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1108/JHTT-05-2022-0141
Kasikorn Research Center. (2022). Digital transformation trends in the Thai F&B sector. KBank.
Kim, C., Mirusmonov, M., & Lee, I. (2010). An empirical examination of factors influencing the intention to use mobile payment. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(3), 310–322. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2009.10.013
Kline, R. B. (2015). Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. (4th ed.). Guilford Press.
Kwortnik, R. J., & Ross, W. T. (2007). The role of positive emotions in experiential decisions. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 24(4), 324–335. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijresmar.2007.09.002
Lee, J., Park, J., & Kim, M. (2023). Brand image and customer loyalty in the digital era: Evidence from the food service industry. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 70, 103070. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2022.103070
Lepp, A., & Gibson, H. (2003). Tourist roles, perceived risk and international tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, 30(3), 606–624. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-7383(03)00024-0
Likert, R. (1932). A technique for the measurement of attitudes. (Archives of Psychology No. 140). The Science Press. Retrieved from https://archive.org/details/likert-1932
Ministry of Commerce, Department of Business Development. (2023). Thailand food service industry outlook 2023. Ministry of Commerce.
Nikopoulou, M., Kourouthanassis, P., Chasapi, G., Pateli, A., & Mylonas, N. (2023). Determinants of digital transformation in the hospitality industry: Technological, organizational, and environmental drivers. Sustainability, 15(3), 2736. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032736
Oliver, R. L. (1999). Whence consumer loyalty?. Journal of Marketing, 63(4), 33–44. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1177/00222429990634s105
Palinkas, L. A., Horwitz, S. M., Green, C. A., Wisdom, J. P., Duan, N., & Hoagwood, K. (2015). Purposeful sampling for qualitative data collection and analysis in mixed method implementation research. Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research, 42, 533–544. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1007/s10488-013-0528-y
Pantano, E., Priporas, C.-V., & Stylos, N. (2017). “You will like it!” Using open data to predict tourists’ response to a tourist attraction. Tourism Management, 60, 430–438. Retrived from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.12.020
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Malhotra, A. (2005). E S QUAL: A multiple item scale for assessing electronic service quality. Journal of Service Research, 7(3), 213–233. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670504271156
Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice. (4th ed.). SAGE Publications.
Schumacker, R. E., & Lomax, R. G. (2016). A beginner’s guide to structural equation modeling. (3rd ed.). Routledge.
Shin, H., & Kang, J. (2020). Reducing perceived health risk to attract hotel customers in the COVID 19 pandemic era: Focused on technology innovation for social distancing and cleanliness. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 91, 102664. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102664
Sivarajah, U., Kamal, M. M., Irani, Z., & Weerakkody, V. (2017). Critical analysis of Big Data challenges and analytical methods. Journal of Business Research, 70, 263–286. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.08.001
Somera, F. A. R., & Petrova, K. (2024). A change management view on technology adoption in hotel organizations: A review and a conceptual framework. Businesses, 4(4), 791–811. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.3390/businesses4040043
Vermeulen, I. E., & Seegers, D. (2009). Tried and tested: The impact of online hotel reviews on consumer consideration. Tourism Management, 30(1), 123–127. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2008.04.008
Vo Thanh, T., Zaman, M., Hasan, R., Akter, S., & Dang Van, T. (2022). The service digitalization in fine dining restaurants: A cost benefit perspective. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 34(9), 3502–3524. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCHM 09 20211130
Yeung, R. M. W., & Morris, J. (2001). Food safety risk: Consumer perception and purchase behaviour. British Food Journal, 103(3), 170–186. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1108/00070700110386728
Yin, R. K. (2018). Case study research and applications: Design and methods. (6th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Zeng, Z., Chen, P. J., & Lew, A. A. (2020). From high touch to high tech: COVID 19 drives robotics adoption. Tourism Geographies, 3, 724-734.Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1080/14616688.2020.1762118
Zeithaml, V. A., Berry, L. L., & Parasuraman, A. (1996). The behavioral consequences of service quality. Journal of Marketing, 60(2), 31–46. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.1177/002224299606000203
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Community and Social Development Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
1. Articles, information, content, images, etc published in the “Community and Social Development Journal” are copyrighted by the Community and Social Development Journal, Chiang Mai Rajabhat University. In order to properly distribute the articles through print and electronic media, the authors still hold the copyright for the published articles under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license, which allows the re-distribution of the articles in other sources. References must be made to the articles in the journal. The authors are responsible for requesting permission to reproduce copyrighted content from other sources.
2. The content of the articles appearing in the journal is the direct responsibility of the article authors. The editorial board of the journal does not necessarily agree with or share any responsibility.













